A key point to understand about essential oils is that they are very concentrated, meaning you only need to use a very small amount to experience results. Essential oils must be used with care and labels must be read carefully so that guidelines are always closely followed.
Here are some of the most frequently asked questions regarding essential oil safety:
Should essential oils be used externally or only topically on skin?
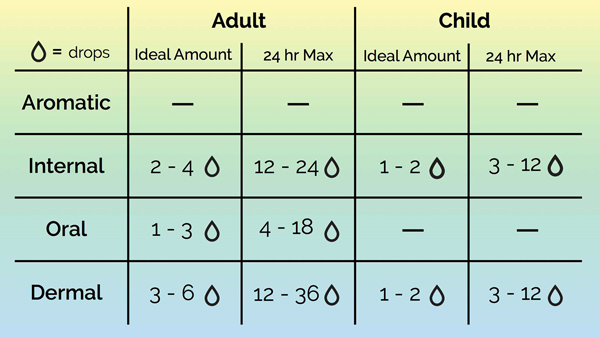
Depending on the specific oil, they can be used in both topically or internally. When applying oil to your skin, it’s usually best to dilute about 2 to 3 drops of pure oil with a vegetable oil that serves as a “carrier oil.” Mix a small amount of the essential oil with equal parts of coconut oil or jojoba oil and then apply to your skin over the affected area that you’re treating. Some of the best locations on the body to use essential oils include on your neck, temples, wrists, over your abdomen, chest and the soles of your feet. Essential oils should never be applied to the eyes or ear canals.
Are essential oils safe to inhale?
Yes, most essential oils are safe to inhale or diffuse. You can diffuse a couple of drops in a diffuser, or inhale the oil directly from the bottle for several seconds. Is it bad to inhale essential oils if you’re already sick? Inhaling certain essential oil vapours can actually help to improve recovery if you’re congested, dealing with a cold or if you have seasonal allergies.
For example, rosemary, peppermint and eucalyptus oil can all help you breath more easily and manage symptoms of respiratory conditions. You can also add 2 drops of oil to boiling water, put a towel over your head and breathe in the aroma for 5 minutes.
Are essential oils safe when used internally and ingested?
This depends on the specific oil. Certain essential oils have been approved as ingredients in food and are classified as GRAS (generally recognized as safe) by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Is it safe to drink essential oils? You can use very small amounts of certain essential oils in water or tea, such as lemon or ginger oil, but in general you should use precaution when taking essential oils internally.
Oils that are generally safe when used both externally & internally include:
- Bergamot — May cause skin sensitivity. Avoid direct sunlight for up to 12 hours after external application. May affect blood sugar control.
- Cassia — May reduce milk supply in lactating women and should only be used in small doses.
- Cilantro
- Cinnamon Bark — May cause skin sensitivity/irritation and should always be tested first by people with sensitive skin.
- Clove — Can cause skin irritation and/or have a numbing effect. May irritate the sinuses and eyes in some people, so use with caution. When using internally take a probiotic supplement twice daily to restore beneficial flora.
- Coriander — May cause skin sensitivity.
- Cumin — Should not be used during pregnancy. Avoid direct sunlight for up to 12 hours after external application.
- Fennel — Do not use during pregnancy.
- Frankincense — Has blood-thinning effects, so people with problems related to blood clotting should not use this oil before consulting with their healthcare provider. Can be diffused, breathe in directly or rubbed topically on the skin.
- Geranium — May cause skin sensitivity. Avoid using it during the first trimester of pregnancy, and use only in topical dilutions thereafter. During pregnancy use with caution since it may influence hormone secretions, especially estrogen.
- Ginger — May cause skin sensitivity.
- Grapefruit — Has been shown to interfere with certain medications, so always ask your doctor. Avoid direct sunlight for up to 12 hours after external application since it can increase sensitivity to sunlight.
- Helichrysum
- Jasmine — Avoid use during pregnancy.
- Juniper Berry—May cause skin sensitivity.
- Lavender
- Lemon — Avoid direct sunlight for up to 12 hours after topical application.
- Lemongrass — May cause skin sensitivity. Should not be used by women who are pregnant, children or nursing mothers.
- Lime — May cause skin sensitivity. Avoid direct sunlight for up to 12 hours after topical application.
- Marjoram — Should not be used during pregnancy.
- Melissa — May cause skin sensitivity. Avoid use during pregnancy.
- Myrrh — Must be avoided during pregnancy. May lower blood sugar levels and interfere with blood sugar conditions.
- Orange — May cause skin sensitivity. Avoid direct sunlight for up to 12 hours after external application to avoid burns or redness.
- Oregano — Avoid use during pregnancy. Not to be used by infants and small children. May cause skin irritation. Should not used for more than 10 days.
- Patchouli —May inhibit blood clotting and pose a drug interaction risk.
- Peppermint — May be taken directly (about 1–2 drops) for digestive support.
- Roman Chamomile — Not recommended for use during pregnancy. Should only be used internally for up to two weeks.
- Rosemary — Do not use if you are pregnant, have high blood pressure or if you’ve been diagnosed with epilepsy.
- Sandalwood — May cause skin sensitivity.
- Spikenard — Should not be used during pregnancy.
- Thyme — Avoid use during pregnancy or if you have high blood pressure or epilepsy.
- Vetiver — May cause skin sensitivity.
- Ylang Ylang
SEE ALL SINGLE ESSENTIAL OILS ON OUR DEDICATED WEBSITE PAGE
- Essential oils are incredibly potent. When you are first introduced to essential oils, it can seem like the bottle size is somewhat underwhelming when compared to the cost. However, over time you will realize that even one drop of essential oil can be effectively used.
- When in doubt—dilute. There are some oils that should always be diluted when using topically: Cassia, Cinnamon, Clove, Geranium, Lemongrass, Oregano, and Thyme. For first time use of any of these “hot” oils, we recommend trying them at a ratio of one drop essential oil to 10 drops of Fractionated Coconut Oil.
- Before using an oil internally, check the label first. Aside from checking online to see if an oil is meant for internal use or not, you can also simply look at the label to find out. If the oil includes supplement facts, it can be used internally. If not, the label will simply say, “For aromatic or topical use.” The single oils that should never be ingested are: Arborvitae, Blue Tansy, Cedarwood, Cypress, Douglas Fir, Eucalyptus, Spikenard, and Wintergreen.
- Be aware of the way some oils react to UV light. Some essential oils cause photosensitivity, which can cause your skin to sunburn more easily. To be safe, after using any of the following oils, avoid UV light of any kind for up to 12 hours after applying. These oils are: AromaTouch, Bergamot, Breathe, Cheer, Citrus Bliss, Elevation, Forgive, Grapefruit, InTune, Lemon, Lime, Motivate, On Guard, Purify, Slim & Sassy, Wild Orange, and Zendocrine.
- Children are more sensitive to oils than adults. When using the oils with babies and children. always dilute the oil and start by only applying oils to their feet. Diffusing oils is the best course of action for using oils with kids under two years of age.
- There are so many uses for oils in everyday life. For whatever reason you started using oils, whether it was to help with wellness or to make your home smell inviting, there are so many ways to use them. They can also be used for cleaning surfaces, doing laundry, helping with emotional health and using them for your beauty routine. Just enjoy them!